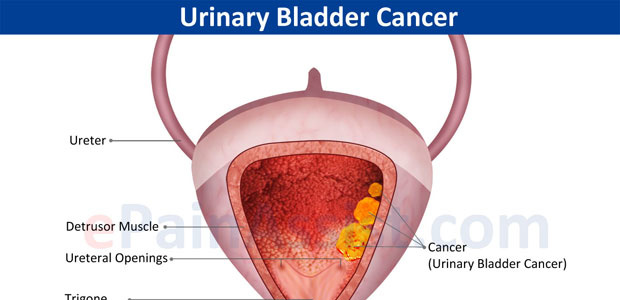
What is bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is one of the most common cancer types in urinary system, arising from mucous membrane of urinary bladder. Epithelial cells of mucous membrane of urinary bladder are also named uroepithelial cells, from which develops urothelioma, a most common malignancy takes up to 90-95% in all kinds of bladder cancer. Other rare bladder cancers include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Staging of urinary bladder cancer
Stage 0: Cancer cells are found only on the inner lining of the bladder.
Stage I: Cancer cells have proliferated to the layer beyond the inner lining of the urinary bladder but not to the muscles of the urinary bladder.
Stage II: Cancer cells have proliferated to the muscles in the bladder wall but not to the fatty tissue that surrounds the urinary bladder.
Stage III: Cancer cells have invaded to the fatty tissue surrounding the urinary bladder and to the prostate gland, vagina, or uterus, but not to the lymph nodes or other organs.
Stage IV: Cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes, pelvic or abdominal wall, and/or other organs.
Recurrent: Cancer has recurred in the urinary bladder or in another nearby organ after having been treated.
What is the incidence of bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer accounts for 3% of all malignant tumors all around the world and over 350,000 people are diagnosed of it each year. It happens in all ages but tends to occur within the age range of 50-60. Moreover, the incidence goes up as age increases and would be 3-4 times higher for male to develop bladder cancer than female.
Bladder cancer is caused by interaction of multiple factors. Smoking and occupational contact of aromatic amine are the main known contributors to urinary bladder cancer. There are other related factors of it.
Carcinogenic substance in drinking water. Taking the water with chloride left through chlorine sterilization would increase the risk of getting bladder cancer.
Diseases of urethra. Long-term and chronic irritation in urothelium or carcinogenic substance from body metabolism increases in urine would result in epitheliosis of urinary tract that cancerization occurs.
Drugs. Take massive doses of a painkiller named phenacetin would increase the risk of bladder cancer too.
- Diet care
A bladder cancer patient should take more fresh fruits and vegetables.
Have diets with high protein, such as eggs, milk and fish and so on.
Adjust the diets according to patient flavor, but spicy food or the diets which are hard for digestion should be forbidden.
- Post-operative care
Keep the ward clean and the air fresh.
Prevent from getting infection and improve the immunity of patient.
Family should always support the patient to help him eliminate the negative emotions.